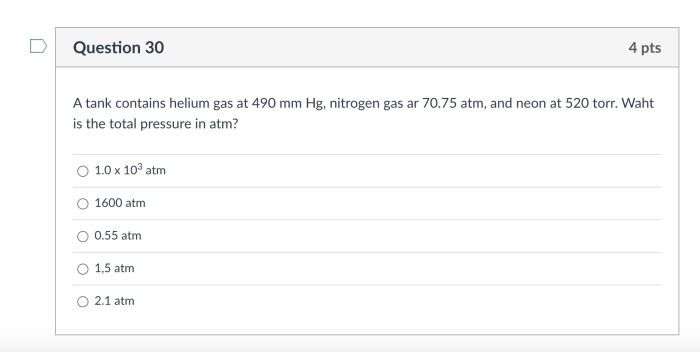
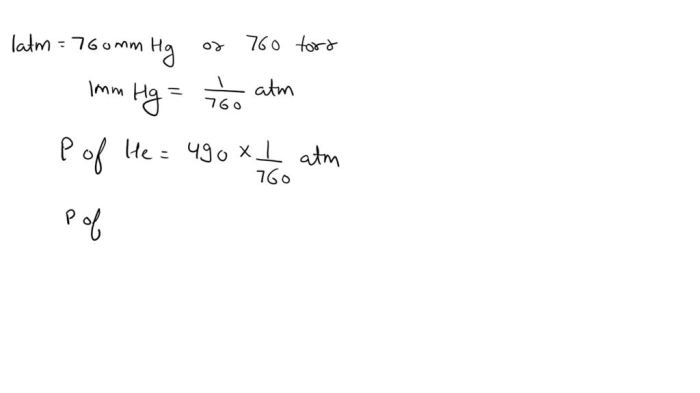A tank contains helium gas at 490 mmHg, inviting exploration into the fascinating realm of gases and their properties. This gas, renowned for its lightness and inert nature, finds diverse applications in fields ranging from medicine to manufacturing. Join us as we delve into the intriguing world of helium gas, examining its characteristics, applications, and safety considerations.
Helium, the second lightest element, possesses unique properties that distinguish it from other gases. Its low density and high thermal conductivity make it an ideal choice for balloons and cryogenic applications. Additionally, its inert nature renders it non-flammable and non-toxic, making it suitable for medical imaging and welding.
Introduction to Helium and its Properties: A Tank Contains Helium Gas At 490 Mmhg
Helium is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the universe. It has a very low density, high thermal conductivity, and is chemically inert. These unique properties make helium useful in a wide variety of applications, including balloons, cryogenics, and medical imaging.
Pressure and Volume Relationships in Gases
The relationship between pressure and volume in gases is described by Boyle’s Law. Boyle’s Law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume, assuming constant temperature. This means that as the pressure of a gas increases, its volume decreases, and vice versa.
Tank Pressure and Gas Volume, A tank contains helium gas at 490 mmhg
The volume of helium gas in a tank at 490 mmHg, assuming standard temperature and atmospheric pressure, can be calculated using Boyle’s Law. The formula is:V1/P1 = V2/P2where:
- V1 is the initial volume of the gas
- P1 is the initial pressure of the gas
- V2 is the final volume of the gas
- P2 is the final pressure of the gas
Plugging in the given values, we get:V1/760 mmHg = V2/490 mmHgSolving for V2, we get:V2 = V1
(490 mmHg / 760 mmHg)
Applications of Helium Gas
Helium gas is used in a variety of industries, including medical imaging, welding, and manufacturing. In medical imaging, helium is used as a contrast agent in MRI scans. In welding, helium is used as a shielding gas to protect the weld from oxidation.
In manufacturing, helium is used to create high-purity atmospheres for semiconductor production.
Safety Considerations with Helium Gas
Helium gas is generally considered to be safe, but there are some potential hazards that should be considered. Helium gas can cause asphyxiation if it displaces oxygen in the air. It can also cause frostbite if it comes into contact with skin.
Helium gas should be handled and stored with care.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the volume of helium gas in a tank at 490 mmHg?
The volume of helium gas in a tank at 490 mmHg can be calculated using Boyle’s Law, assuming standard temperature and atmospheric pressure.
What are the potential hazards associated with handling helium gas?
Helium gas can pose potential hazards, including asphyxiation and frostbite. Proper handling and storage guidelines must be followed to ensure safety.
What are the common applications of helium gas?
Helium gas finds applications in various industries, including medical imaging, welding, manufacturing, and scientific research.