With maritime empires significance ap world history at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
The emergence of maritime empires has profoundly shaped the course of world history, leaving an enduring legacy that continues to resonate today. From the ancient Phoenicians to the Portuguese and Spanish explorers of the Age of Discovery, maritime empires have played a pivotal role in global trade, cultural exchange, and political transformation.
Emergence and Spread of Maritime Empires
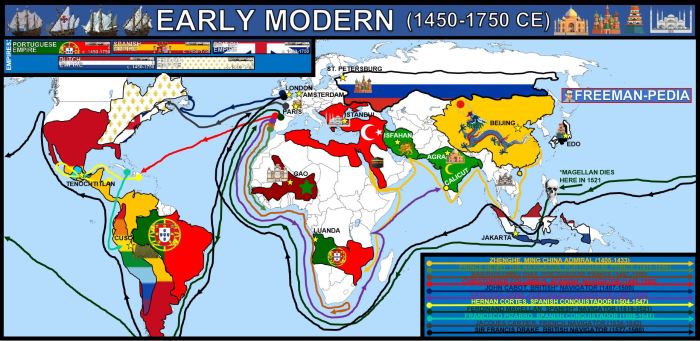
Maritime empires emerged in world history due to technological advancements, economic motivations, and political ambitions. These empires flourished in geographical regions with access to major sea routes and favorable winds, such as the Mediterranean Sea, the Indian Ocean, and the Atlantic Ocean.
Factors Contributing to the Rise of Maritime Empires
- Technological advancements, including the development of ships and navigational instruments
- Economic motivations, such as the search for new trade routes and resources
- Political ambitions, such as the desire to expand territories and establish dominance
Geographical Regions Where Maritime Empires Flourished, Maritime empires significance ap world history
- Mediterranean Sea: Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans
- Indian Ocean: Arabs, Chinese, Indians
- Atlantic Ocean: Portuguese, Spanish, British
Economic and Commercial Impact of Maritime Empires
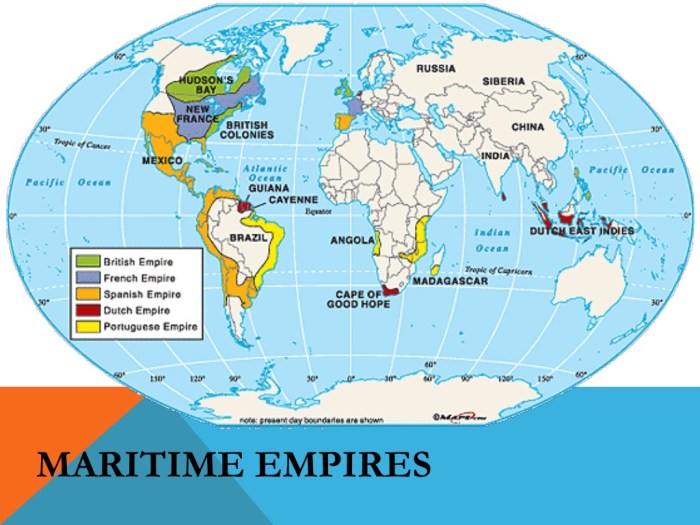
Maritime empires transformed global trade networks by establishing new trade routes and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. This trade played a significant role in the development of capitalism and the emergence of a global economy.
Impact on Global Trade Networks
- Established new trade routes connecting different parts of the world
- Facilitated the exchange of a wide range of goods, including spices, textiles, and luxury items
- Spread new ideas and technologies, such as printing and gunpowder
Role in the Development of Capitalism
- Increased trade led to the accumulation of wealth and the rise of merchant classes
- Stimulated the development of banking and financial systems
- Contributed to the emergence of a global market economy
Examples of Commodities and Trade Routes
- Spice trade: Portuguese and Dutch empires controlled the spice trade routes from Asia to Europe
- Slave trade: British and French empires were involved in the transatlantic slave trade
- Tea trade: British East India Company monopolized the tea trade between China and Europe
Cultural and Social Transformations
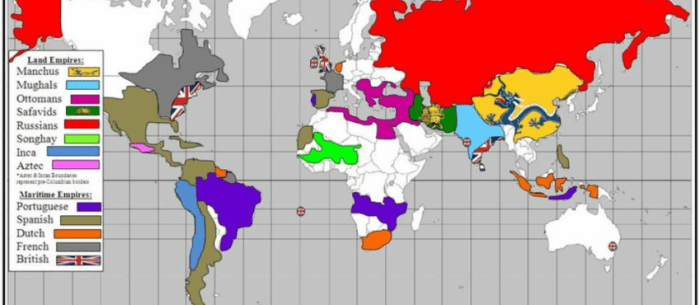
Maritime empires brought about cultural exchanges between different civilizations, influencing art, literature, religion, and social customs. These interactions led to cultural syncretism and the spread of ideas across different regions.
Cultural Exchanges
- Exchange of artistic styles and techniques, such as the influence of Chinese porcelain on European ceramics
- Spread of new religions, such as the introduction of Christianity to the Americas by European colonizers
- Adoption of new social customs, such as the use of tea in Europe after its introduction by the British East India Company
Cultural Syncretism
- Creation of new cultural forms that blended elements from different cultures, such as the Baroque architectural style in Latin America
- Spread of ideas and philosophies, such as the influence of Indian philosophy on European thought
- Emergence of hybrid identities, as people from different cultures interacted and intermarried
Political and Military Implications: Maritime Empires Significance Ap World History
Maritime empires expanded their territories through conquest and colonization, establishing colonies and implementing various forms of control and governance. These empires had a significant impact on local political structures and the balance of power.
Expansion and Colonization
- Established colonies in different parts of the world, such as the British colonies in North America and the French colonies in Africa
- Controlled vast territories and resources, leading to economic and political dominance
- Spread European political systems and ideologies to other regions
Methods of Control and Governance
- Direct rule: Imposing imperial laws and administration on colonies
- Indirect rule: Allowing local rulers to govern under the supervision of imperial authorities
- Economic exploitation: Extracting resources and wealth from colonies
Impact on Local Political Structures
- Disrupted existing political systems and power structures
- Introduced new forms of government and administration
- Created tensions and conflicts between imperial authorities and local populations
Top FAQs
What were the primary factors that contributed to the emergence of maritime empires?
Technological advancements, economic motivations, and political ambitions were key factors in the rise of maritime empires.
How did maritime empires impact global trade networks?
Maritime empires transformed global trade networks, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies across vast distances.
What were some of the cultural consequences of maritime exploration and trade?
Cultural exchanges between maritime empires and indigenous populations led to the spread of ideas, artistic influences, and religious beliefs.
How did maritime empires contribute to environmental challenges?
Maritime exploration and trade introduced invasive species, exploited natural resources, and contributed to deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
What factors led to the decline and fall of maritime empires?
Internal political instability, external challenges, economic pressures, and technological advancements all played a role in the decline and fall of maritime empires.