General intelligence ap psychology definition serves as the cornerstone of this exploration, providing a comprehensive overview of the concept, its historical evolution, and its multifaceted nature within the realm of AP Psychology.
This discourse delves into the various components that constitute general intelligence, examining fluid and crystallized intelligence, and presents examples to illustrate their measurement.
Definition of General Intelligence in AP Psychology

General intelligence (g) is a construct that refers to a person’s overall intellectual abilities. It is often measured using IQ tests and standardized achievement tests. The concept of g has been studied by psychologists for over a century, and there is still much debate about its nature and structure.
Historical Development of the Concept of g, General intelligence ap psychology definition
The concept of g was first proposed by Charles Spearman in 1904. Spearman conducted a study of school children’s performance on a variety of cognitive tasks and found that there was a strong positive correlation between their performance on all of the tasks.
He concluded that this correlation was due to a single underlying factor, which he called g.
Components of General Intelligence
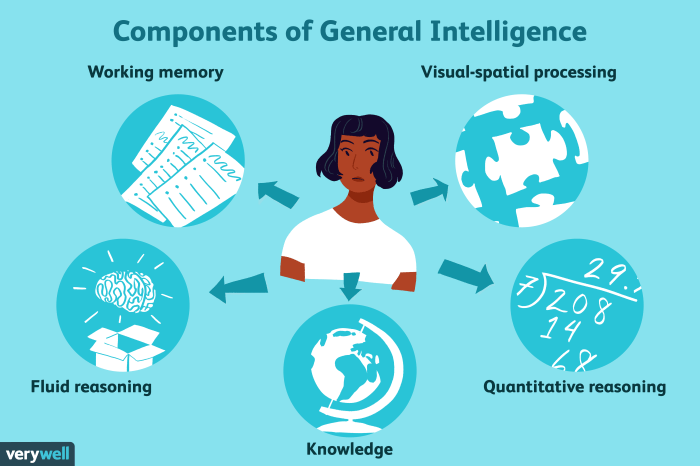
General intelligence is thought to be composed of a number of different components, including:
- Fluid intelligence: This is the ability to think abstractly, solve problems, and reason. It is often measured by tasks such as Raven’s Progressive Matrices and the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS).
- Crystallized intelligence: This is the ability to use knowledge and experience to solve problems. It is often measured by tasks such as vocabulary tests and reading comprehension tests.
Theories of General Intelligence
There are a number of different theories that attempt to explain the nature of general intelligence. Two of the most common theories are:
- The two-factor theory: This theory, proposed by Charles Spearman, suggests that general intelligence is composed of two factors: g and s. G is a general factor that is responsible for performance on all cognitive tasks, while s is a specific factor that is responsible for performance on specific tasks.
- The hierarchical model: This theory, proposed by L.L. Thurstone, suggests that general intelligence is composed of a number of different factors, each of which is responsible for a specific type of cognitive task.
Measurement of General Intelligence
General intelligence is typically measured using IQ tests and standardized achievement tests. IQ tests are designed to measure a person’s overall intellectual abilities, while standardized achievement tests are designed to measure a person’s knowledge and skills in specific academic areas.
IQ tests are typically administered by psychologists and other trained professionals. They consist of a series of questions that are designed to measure a person’s reasoning, problem-solving, and verbal abilities.
Standardized achievement tests are typically administered in schools and other educational settings. They consist of a series of questions that are designed to measure a person’s knowledge and skills in specific academic areas, such as reading, writing, and mathematics.
Genetics and Environment in General Intelligence
The development of general intelligence is influenced by both genetics and environment. Studies have shown that there is a significant heritability for intelligence, meaning that intelligence is passed down from parents to children through genes.
However, environment also plays a role in the development of intelligence. Children who grow up in stimulating and supportive environments tend to have higher IQ scores than children who grow up in impoverished and neglectful environments.
Cultural Influences on General Intelligence
Cultural factors can also influence the measurement and interpretation of general intelligence. For example, children who grow up in cultures that value education and intellectual achievement tend to have higher IQ scores than children who grow up in cultures that do not value education.
It is important to note that cultural factors can also affect the way that intelligence is measured. For example, IQ tests that are designed for use in Western cultures may not be appropriate for use in non-Western cultures.
General Inquiries: General Intelligence Ap Psychology Definition
What is the concept of general intelligence (g) in AP Psychology?
General intelligence (g) in AP Psychology refers to a broad cognitive ability that encompasses various mental processes, including reasoning, problem-solving, and learning.
What are the different components of general intelligence?
General intelligence comprises two primary components: fluid intelligence and crystallized intelligence. Fluid intelligence involves the ability to reason and solve problems independently of prior knowledge, while crystallized intelligence represents accumulated knowledge and skills.
