Carbon capture storage pros and cons – Carbon capture storage (CCS) emerges as a topic of significant importance in the fight against climate change. With the potential to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, CCS has sparked discussions about its advantages and disadvantages. This article delves into the pros and cons of CCS, examining its role in reducing carbon emissions and the challenges it faces.
CCS technologies offer promising solutions for capturing carbon dioxide from industrial processes and storing it underground. By preventing the release of these emissions into the atmosphere, CCS contributes to climate change mitigation efforts. However, concerns regarding the costs, environmental risks, and long-term storage safety of CCS raise questions about its feasibility and widespread adoption.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)

Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a set of technologies aimed at capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes or directly from the atmosphere and storing it underground. The goal of CCS is to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
paragraphCCS technologies involve capturing CO2 from various sources, including power plants, industrial facilities, and the air. The captured CO2 is then transported to suitable geological formations, such as deep saline aquifers, depleted oil and gas reservoirs, and unmineable coal seams, where it is injected and stored.
CCS Technologies
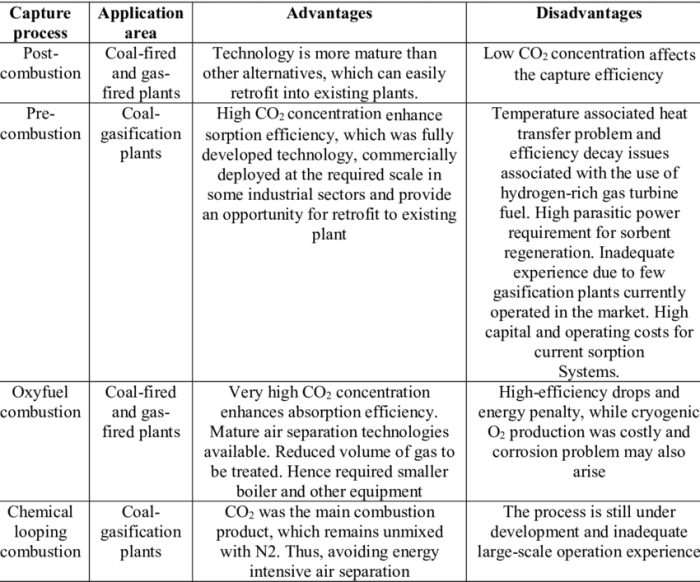
- Pre-combustion capture:Involves capturing CO2 from the fuel before it is burned.
- Post-combustion capture:Captures CO2 from the exhaust gases after fuel combustion.
- Oxyfuel combustion:Burns fuel in pure oxygen instead of air, resulting in a concentrated CO2 stream.
- Direct air capture (DAC):Captures CO2 directly from the atmosphere using various technologies.
Applications of CCS
- Power generation:CCS can be integrated into power plants to capture CO2 emissions.
- Industrial processes:CCS can be applied to industries that produce large amounts of CO2, such as cement and steel manufacturing.
- Bioenergy with CCS (BECCS):Combines biomass combustion with CCS to achieve negative emissions.
- Enhanced oil recovery (EOR):Injected CO2 can help extract additional oil from reservoirs.
Pros of CCS

Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) offers promising advantages in the fight against climate change. Its potential to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to sustainable energy solutions makes it a valuable tool in the transition towards a low-carbon future.
CCS technology captures carbon dioxide (CO2) from industrial processes or power plants, preventing its release into the atmosphere. This captured CO2 is then transported and stored underground in geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or deep saline aquifers.
Case Studies of Successful CCS Implementations
Numerous successful CCS projects have demonstrated the technology’s feasibility and effectiveness. One notable example is the Sleipner project in Norway, which has been capturing and storing CO2 from a natural gas processing plant since 1996. The project has successfully stored over 20 million tonnes of CO2, making it one of the largest CCS projects in operation.
Another successful implementation is the Boundary Dam Power Station in Canada, which captures CO2 from a coal-fired power plant. The captured CO2 is used for enhanced oil recovery, demonstrating the potential for CCS to contribute to both climate change mitigation and economic benefits.
Contribution to Climate Change Mitigation
CCS plays a crucial role in climate change mitigation by reducing the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere. By capturing and storing CO2 from industrial sources and power plants, CCS can significantly contribute to the global efforts to limit greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
CCS is particularly valuable in sectors where decarbonization is challenging, such as heavy industries and power generation. It provides a practical solution for reducing emissions from these sectors, helping to bridge the gap towards a net-zero emissions future.
Cons of CCS
While CCS holds promise as a potential climate change mitigation strategy, it also faces several challenges and potential drawbacks.
One major concern is the high cost associated with CCS. The process of capturing, transporting, and storing CO 2is energy-intensive and requires significant infrastructure investments. This can make CCS a less cost-effective option compared to other renewable energy sources or energy efficiency measures.
Environmental Risks, Carbon capture storage pros and cons
CCS also raises environmental concerns. The process of capturing CO 2can release other pollutants into the atmosphere, such as nitrogen oxides (NO x) and sulfur oxides (SO x). Additionally, there are concerns about the potential for CO 2leakage from geological storage sites.
While geological storage is generally considered safe, there is a risk that CO 2could escape over time, potentially contaminating groundwater or contributing to climate change.
Failed and Controversial Projects
There have been several notable failed or controversial CCS projects. One example is the FutureGen project in the United States, which aimed to demonstrate a large-scale CCS system. However, the project was canceled in 2015 due to cost overruns and technical challenges.
Economic Considerations: Carbon Capture Storage Pros And Cons

Carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects involve significant costs and financial implications. The upfront capital investment required for CCS technology is substantial, including expenses for capture equipment, compression facilities, transportation infrastructure, and geological storage sites.
Cost-Effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness of CCS varies depending on factors such as the scale of the project, the capture technology employed, and the geological conditions of the storage site. While CCS can be more expensive than some other emission reduction strategies, such as renewable energy or energy efficiency measures, it offers a unique advantage in capturing and storing large volumes of CO 2from industrial processes and power plants, where other options may not be feasible.
Government Incentives
To promote the adoption of CCS technology, governments have implemented various incentives and policies. These include tax credits, subsidies, and loan guarantees. Such incentives can help reduce the financial burden of CCS projects and make them more economically viable for industries and investors.
Environmental Impacts
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but it also raises environmental concerns. This section assesses the potential environmental impacts of CCS, both positive and negative, and discusses concerns about the long-term effects of geological storage.
One of the main environmental benefits of CCS is that it can help to reduce air pollution. The capture of CO 2from power plants and other industrial sources can reduce emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO 2), nitrogen oxides (NO x), and particulate matter (PM).
These pollutants can cause respiratory problems, heart disease, and other health issues.
CCS can also help to reduce water pollution. The capture of CO 2from power plants can reduce the amount of wastewater that is produced. This wastewater can contain pollutants such as heavy metals and other toxic chemicals.
However, there are also some potential environmental risks associated with CCS. One concern is that the geological storage of CO 2could lead to the contamination of groundwater. If CO 2leaks from a storage site, it could dissolve into groundwater and make it acidic.
This could harm aquatic life and make the water unsafe for drinking.
Another concern is that the geological storage of CO 2could lead to the release of other harmful gases, such as methane. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, and its release could offset the climate benefits of CCS.
Overall, the environmental impacts of CCS are complex and uncertain. There are both potential benefits and risks associated with this technology. Further research is needed to better understand the environmental impacts of CCS and to develop strategies to mitigate the risks.
Concerns about the long-term effects of geological storage
One of the main concerns about CCS is the long-term effects of geological storage. CO 2is a stable gas, and it can remain in geological formations for thousands of years. There is concern that CO 2could leak from storage sites and enter the atmosphere, where it would contribute to climate change.
There are a number of factors that could affect the long-term stability of CO 2storage sites. These factors include the geological formation itself, the depth of the storage site, and the pressure of the CO 2. The most suitable geological formations for CO 2storage are deep, stable, and impermeable.
The depth of the storage site is also important, as the pressure of the overlying rock helps to keep the CO 2in place.
There have been a number of studies that have investigated the long-term stability of CO 2storage sites. These studies have shown that CO 2can be stored safely and securely in geological formations for thousands of years. However, it is important to note that these studies have been conducted on a small scale.
It is not yet known how CO 2will behave in large-scale storage sites.
Further research is needed to better understand the long-term effects of geological storage. This research should focus on identifying the factors that could affect the stability of storage sites and developing strategies to mitigate the risks.
How CCS can contribute to a sustainable energy future
CCS has the potential to make a significant contribution to a sustainable energy future. By capturing and storing CO 2from power plants and other industrial sources, CCS can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
CCS is also a relatively affordable technology. The cost of CCS is comparable to the cost of other low-carbon technologies, such as renewable energy and nuclear power. This makes CCS a cost-effective option for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
In addition, CCS is a scalable technology. CCS can be deployed at a large scale, which makes it a viable option for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from a variety of sources.
Overall, CCS has the potential to make a significant contribution to a sustainable energy future. CCS is a safe, affordable, and scalable technology that can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
Technological Advancements

Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in CCS technologies, driven by the urgent need to address climate change. These innovations focus on improving efficiency, reducing costs, and exploring novel approaches.
Emerging Technologies
Among the emerging technologies with promising potential are:
- Direct Air Capture (DAC):DAC systems capture CO2 directly from the atmosphere, offering a potential solution for capturing emissions from sources that lack traditional capture points.
- Carbon Mineralization:This process involves reacting CO2 with minerals to form stable carbonate compounds, providing a permanent storage option.
- Electrochemical CO2 Conversion:Electrochemical methods use electricity to convert CO2 into valuable products such as fuels or chemicals, potentially creating new revenue streams.
Efficiency and Cost Improvements
Ongoing research and development efforts aim to enhance the efficiency of CCS systems, reducing energy consumption and operating costs. This includes optimizing capture processes, improving solvent performance, and developing new materials for storage.
Future Prospects
The future of CCS holds great promise, with continued technological advancements expected to make it a more viable and cost-effective solution. The development of modular and scalable systems, along with innovative storage options, will further contribute to the widespread adoption of CCS.
Public Perception and Policy
Public perception and government policies play a crucial role in shaping the adoption and implementation of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technologies.
Public Attitudes and Perceptions
Public attitudes towards CCS vary widely, influenced by factors such as perceived risks, environmental concerns, and economic implications. Some individuals may be hesitant about CCS due to potential environmental impacts, while others may view it as a necessary solution to climate change.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations can significantly impact CCS adoption. Governments can provide financial incentives, establish regulatory frameworks, and promote public engagement to support the development and deployment of CCS technologies. Clear and consistent policies are essential for creating a favorable investment climate for CCS projects.
Successful Public Engagement and Outreach Programs
Successful public engagement and outreach programs are crucial for building public trust and support for CCS. These programs can involve public forums, educational campaigns, and community involvement initiatives. They aim to provide accurate information, address concerns, and foster dialogue among stakeholders.
Query Resolution
What is the primary goal of carbon capture storage (CCS)?
CCS aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capturing carbon dioxide from industrial processes and storing it underground, preventing its release into the atmosphere.
Are there any successful examples of CCS implementation?
Yes, several CCS projects have been implemented worldwide, such as the Sleipner project in Norway and the Boundary Dam project in Canada, which have demonstrated the feasibility of capturing and storing carbon dioxide.
What are the main concerns associated with CCS?
Concerns include the high costs of CCS projects, the potential for geological storage leakage, and the long-term environmental impacts of carbon dioxide storage.